
Set Focal length and radius (f/stops) to adjust the depth. Landscape Photography: From Snapshots to Great Shots, Rob Sheppard, 2012. Either select an object to be your focal point or set the distance. If you set the camera's focus to the hyperfocal distance, your depth of field will extend from half of the hyperfocal distance to infinity-a much deeper depth of field.Ĭomplete Digital Photography, Ben Long, 2012.Īnother important control for landscape photography is depth of field, the amount of sharpness in a scene, from close to the camera into the distance away from the camera. For example, comparing a 28mm lens with a 50mm lens at the same aperture and shooting distance, depth of field is deeper with the 28mm lens.
DEPTH OF FIELD AND F STOP HOW TO
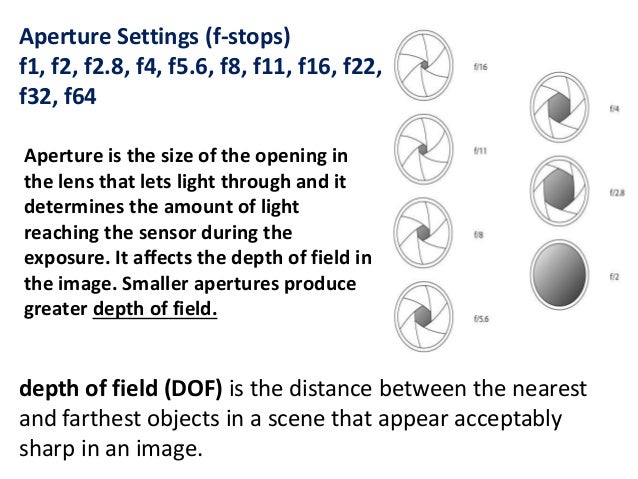
How to Use Your Camera, New York Institute of Photography, 2000. Aperture is the part of the lens that controls the amount of light passing through to the cameras sensor, and its one of the simplest ways to control the depth. is simply a fancy term that means the distance setting at any aperture that produces the greatest depth of field. The Camera (Ansel Adams Photography, Book 1), Ansel Adams, Tenth Edition, 1995 This total region of adequate focus represents the Photograph and the degree of enlargement of the negative). In addition, there will be an area just in front of and behind this plane that will appear reasonably sharp (according to the standards of sharpness required for the particular We can achieve critical focus for only one plane in front of the camera, and all objects in this plane will be sharp. For example, if you have a bigger aperture. The rule is simple: the smaller the aperture (that is, the bigger the f-number), the greater the depth of field. A deep depth of field will keep most of the scene relatively sharp. A very shallow depth of field blurs everything but the point you focus on. Depth of field is the amount of your photo that appears sharp from front to back.
DEPTH OF FIELD AND F STOP MANUAL
For a more in depth explanation of what the aperture settings change check out the Blender manual.Įxternal Content: Camera - Blender Manual

We can mainly just focus on focal length and focus distance if we don't have a focus object. The preview makes it much easier to adjust the look of the depth of field. Note that both the Eevee and Cycles rendered previews allow us to preview the Blur. Unlike a real camera we basically just use the F-stop value to adjust the range from the focal point object or distance that is in focus. We can directly set the object we want the camera to be focused on. With blender we don't have to really worry as much about how we setup our camera.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
